Opening a workbook lets you use a workbook that you or someone else has previously created and then saved. This lesson explains how to open a saved workbook, as well as non-Excel files.
You can locate a workbook on your computer and simply double-click it to open it, but you can also open a workbook from within the Excel program.
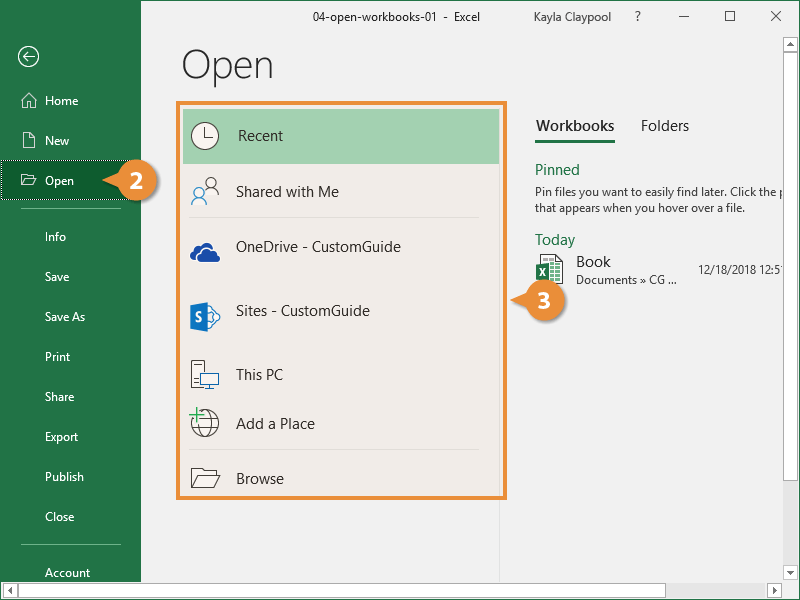
- Click the File tab.
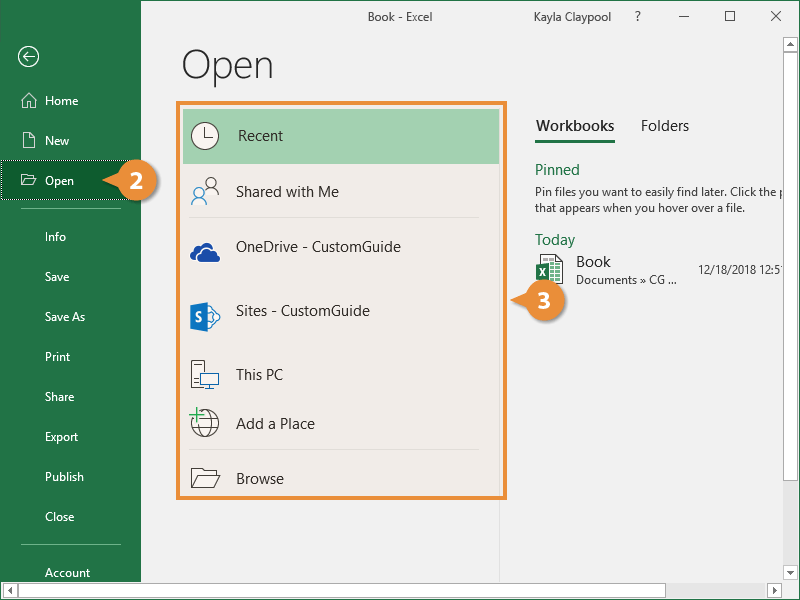
- Click Open.
Press Ctrl + O to quickly display the Open tab of the Backstage view.
- Select the location where the file is saved.
You can choose from:
- Recent: Recent files you've worked on.
- Shared with Me: Files others have shared with you on OneDrive or SharePoint Online.
- OneDrive: Microsoft's cloud-based storage.
- This PC: Browse files on your local computer.
- Browse: Opens a dialog box where you can browse through your computer's folders, drives, and network shares.
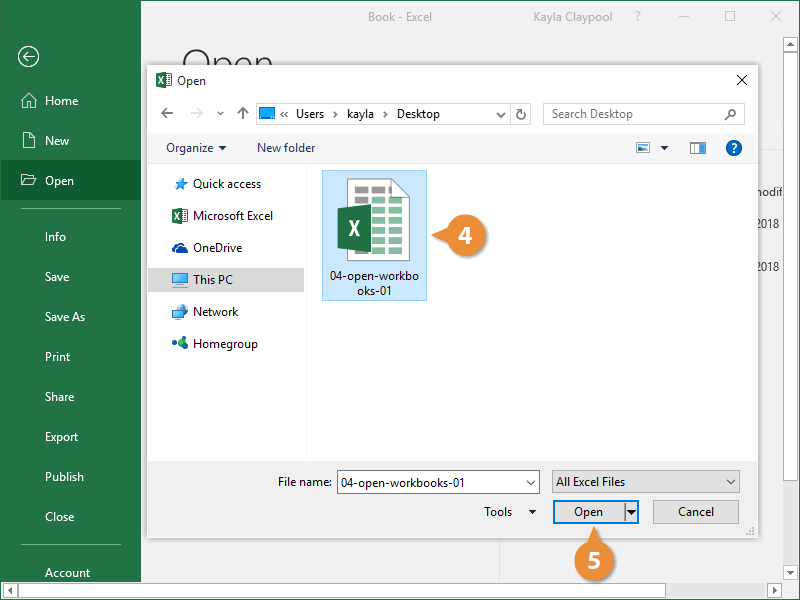
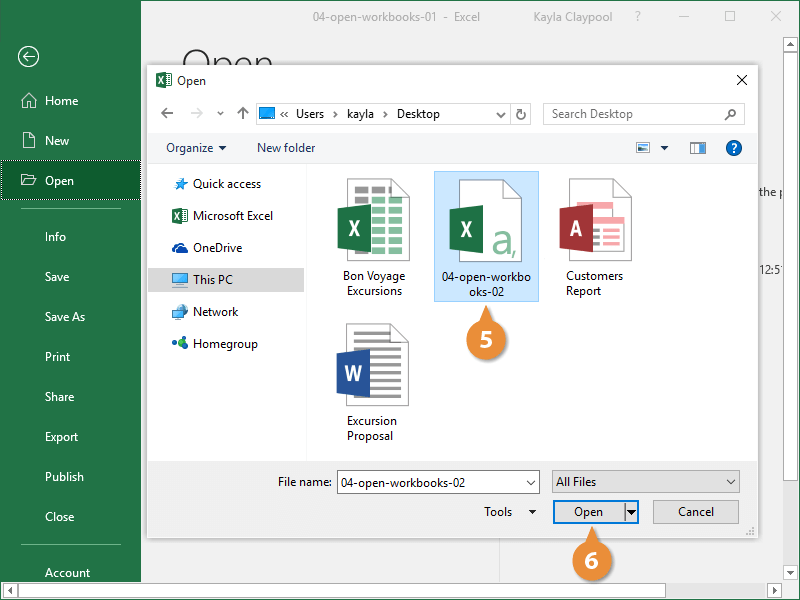
- Select the file you want to open.
- Click Open.
You can also use Excel to open data files created in other programs, like Comma Separated Values or CSV files.
- Click the File tab.
- Click Open.
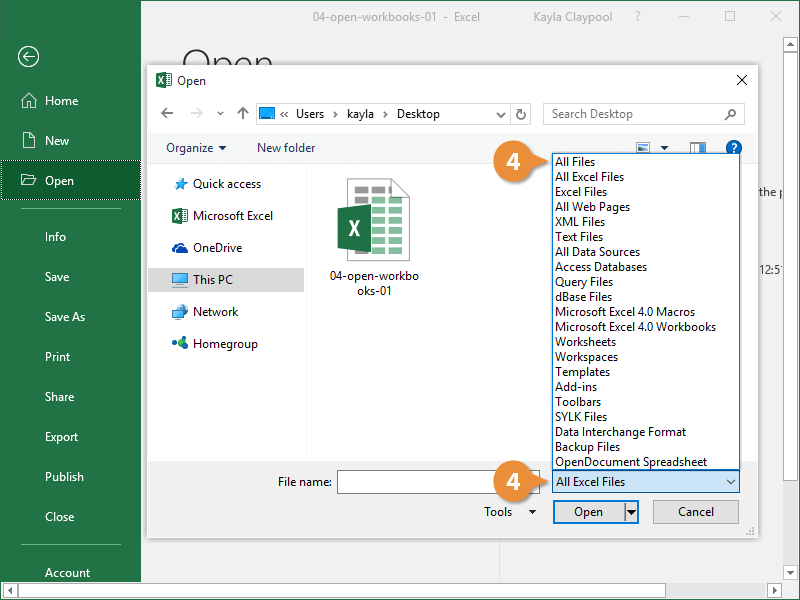
- Select the location where the file is saved.
- Click the file type list arrow and select All Files.
- Select the file you want to open.
- Click Open.
- If prompted, complete the steps in the Text Import Wizard.
| Common File Types |
File Extensions |
Description |
| All Files |
(Any) |
Displays all file types (although Excel might not be able to open all of them). |
| All Excel Files |
.xls and related |
Displays Excel workbooks, templates, and macro-enabled files. |
| All Web Pages |
.htm and related |
Displays web pages, including supporting files such as images. |
| Text Files |
.txt and .csv |
Displays comma and tab delimited text files, often used to import / export data. |
| All Data Sources |
(Varies) |
Displays databases (e.g. Microsoft Access) and queries. |
| Templates |
.xlt and related |
Displays Excel template files. |